How to Identify a Drug Overdose
Drug abuse
can result in serious health complications that may include overdose among
other side effects like addiction. Drug overdose may fall into either
intentional or accidental categories. Intentional overdoses in most cases occur
when someone triesto commit suicide. On the other hand, Accidental overdoses in
most cases occur when somebody takes more than the prescribed medication by the
doctor or when they use too much of a drug to get ‘high’.
Drug
overdose can be identified by physical examination of signs and symptoms, among
other procedures. Such procedures are as discussed below:
Identification of signs and symptoms
The signs
and symptoms of drug overdose may vary from one person to another and also
depend on the drug ingested. Common signs of a drug overdose may include:
·
Abnormal
breathing
·
Vomiting
and nausea
·
Abnormal
body temperature
·
Abnormal
pulse rate
·
Stomach
problem
·
Abnormal
blood pressure, either high or low
·
Dizziness
·
Anxiety
·
Dilated
pupils
·
Death
Someone may
not necessarily exhibit all or most of the signs and symptoms, but if he/she
depicts a few, this may indicate an overdose.
Let’s
discuss some of the featured signs and symptoms in depth to see the DOs and DON’Ts
when a friend or a stranger is under such a situation.
Pulse Rate
Pulse rate
refers to the number of times a heart beats per minute. Many factors may influence
your heart rate but increased pulse rate accompanied by other drug overdose
signs can help identify if one has taken an overdose of a certain drug.
An unusual
low or high pulse rates indicates an underlying body problem. Different drugs
have different effects on heart (pulse) rate, either decreased or increase.
Several drugs such as inhalantsand narcotics result in decreased pulse rate
among other signs. Several other drug overdoses resulting in increased heart
rate includestimulants.
Respiratory rate
This refers
to the number of breathes per minute or inspirations and expirations per any
given unit time. Different activities such as engaging in vigorous physicaltasks
can increase respiration rate, but if all these factors have been ruled out,
drug overdose may be the cause of increased respiratory rate. Stimulants can
cause increased pulse rate, which in turn increases respiratory rate. Other
causes may include:
·
Emotional
causes such as Nervousness and Anxiety, panic attacks, and Stress
·
Medical
causes such as bleeding, infections, pregnancies, severe pain, and lung
diseases e.g. asthma
Blood Pressure
Blood
pressure can be defined as the strength by which the blood pushes against blood
vessels as it is pumped around our bodies for energy and oxygen needed.
Ideal/normal blood pressure for a health human being below 120/80 mmHg. At this
level we have low chances of contracting stroke or a heart disease. Some over
the counter drugs and some other substances such as supplements can have an
adverse effect on your blood pressure. Below is a list of some supplements,
substances and medications that can result to an increase in your blood
pressure.
·
Antidepressants-
Some examples of antidepressantsthat can result in an increase in your blood
pressure include Tricyclic antidepressants, Fluoxetine, and venlafaxine among
others that change our response to brain chemicals that affect our moods.
·
Caffeine-
Caffeine may increase your blood pressure when taken in large quantities by
temporarily blocking a hormone basically responsible for keeping our blood
vessels widened. Examples of caffeine-containing substances or medications
include coffee and other beverages, energy drinks, and caffeine pills.
·
Pain
medications- Some examples of pain medications such as paracetamol and opioids
can also increase blood pressure when taken in quantities higher than
prescribed. Blood pressure increases mainly due to increased pulse rate and
constriction of blood vessels
Abnormal Breathing
Abnormal
breathing also termed as labored respiration/breathing can be defined as a
respiratory problem characterized by increased hardship to breathe. It is
important to note the difference between abnormal breathing from shortness of
breath (dyspnea) which is a simply a respiratory distress sensation.
Abnormal
breathing can sometimes be caused by ingestion of some drugs and overdose of
others. Breathe shortness is an example of abnormal breathing that can be
caused by overdose of some drugs and side effects of other drugs used at normal
dose.
Smoking can
be associated with serious respiratory problems such as breath shortness due to
blockage of air pathways. It is important to also note that abnormal breathing
can be associated with other conditions such as lung and heart conditions.
Therefore, other overdose symptoms and signs can help rule out diseases or
illnesses that may affect your breathing.
Stomach Problem
A stomach
problem or simply a stomach ache is a term referring to cramps or pain in the
abdomen.Common stomach problems associated with drug overdose include:
·
Trapped
wind(with bloating) resulting in discomfort
·
Constipation
·
Discomfort
or pain after eating(indigestion)
In most
cases, drug ingestion results instomach complications such as abdominal cramps,
vomiting and diarrhea. This can lead to serious body fluid loss resulting in
dehydration which in turn if not taken care of immediately, can result in
death. Other common stomach signs and symptoms of drug overdose include:
·
Vomiting
blood
·
Being
unable to breathe
·
Having
black or bloody stools
·
Feeling
pain when you touch your stomach
Other Methods
Other
methods that can be used to identify drug overdose include:
·
Drug
screening
·
Information
from family members about the type and amount of drug you take
Prevention of Drug Overdose
Not taking
drugs in an inappropriate manner at all is the best method to avoid an
overdose. But if it happens to you or someone you care for, following these
simple steps will prove helpful to decrease the chances and probability of an
overdose.
·
Increasing
drug awareness, signs, and risks.
·
Understand
the dosage and drugs to take
·
Use
a low dose after a while of not using
·
In
the case of a drug addiction, seek treatment for substance abuse
When to seek Medical Care
Your doctor, emergency department, local
hospital, or poison center can help you determine the seriousness of a
suspected drug overdose. In case you develop any symptoms related to drug
overdose such as the ones discussed in the article, you should seek immediate
medical help to get better treatment.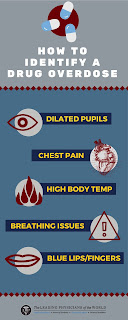




Comments
Post a Comment